Most parents strive to give their children the best educational quality for schooling possible. However, if it is an average family, they cannot afford to spend unreasonable amounts of money on tuition fees. In this case, the child’s parents can opt for a public charter school if they want to get something in between a regular public school and a private school. Today, we’ll look at the difference between charter and private school and help you understand what option is worth consideration.
Making the right school choice: Factors to consider for parents
To begin with, we will give you a small roadmap and then, in more detail, tell you the exact difference between a charter school and a private school, i.e., what factors you should pay special attention to.
- School funding
- Tuition fees
- Admission process
- Curriculum peculiarities
- Educational quality and teacher credentials
Difference Between a Charter School and a Private School: Funding Sources
There is a great difference between a charter school and a private school in funding sources. Private schools rely mainly on tuition fees, charitable contributions, donations, and sometimes religious affiliation as a school funding base. Tuition fees at private schools can range from moderate to extremely high, leaving them affordable for families with higher incomes. Even though they may have scholarships and grants available, these are often incredibly competitive.
In contrast, charter schools are public institutions that operate independently. They receive school funding from federal, state, and local governments, just like traditional public schools. Unlike private schools, charter schools do not charge tuition fees and strive to provide free education to diverse student demographics.
Difference Between Private and Charter School: Tuition Fees and Accessibility
What’s the difference between a private school and a charter school in terms of tuition fees? In this regard, the difference between them is most obvious. The average annual tuition fee for a K-12 private school in the United States was $12,350 in 2021. In most cases, such costs are out of reach for student demographics from lower-income families.
On the contrary, charter schools do not charge tuition fees and are designed to provide diversity in education. However, the availability of charter schools can vary due to demand and limited openings.

Difference Between Charter and Private School: Admission Process and Student Diversity
What is the difference between a charter school and a private school in terms of the admission process? There are many distinctions, as a matter of fact. We have summarized the most important ones for you below.
Private schools:
- Private schools often have strict admission criteria. Typically, they require good SAT or ACT scores, high GPAs, and interviews before accepting students.
- Enrollment in private schools is often selective, favoring learners with high academic achievements or special abilities.
- This selective process sometimes leads to less diversity in the student body. The admission process may give preference to those with high financial means or special academic accomplishments.
- Public school funding comes from hefty tuition fees and donations from alumni and current students.
Charter schools:
- Charter schools work differently in terms of the admission process. They are open to all students within a given territory or district without consideration of their academic preparation or financial status.
- They are required by law to maintain an open enrollment policy.
- If a charter school reaches the maximum number of students, additional students are usually selected through a lottery.
- Charter school funding comes from either state or federal budgets. Public charter schools have no tuition fees.
Student demographics: Who attends charter and private schools?
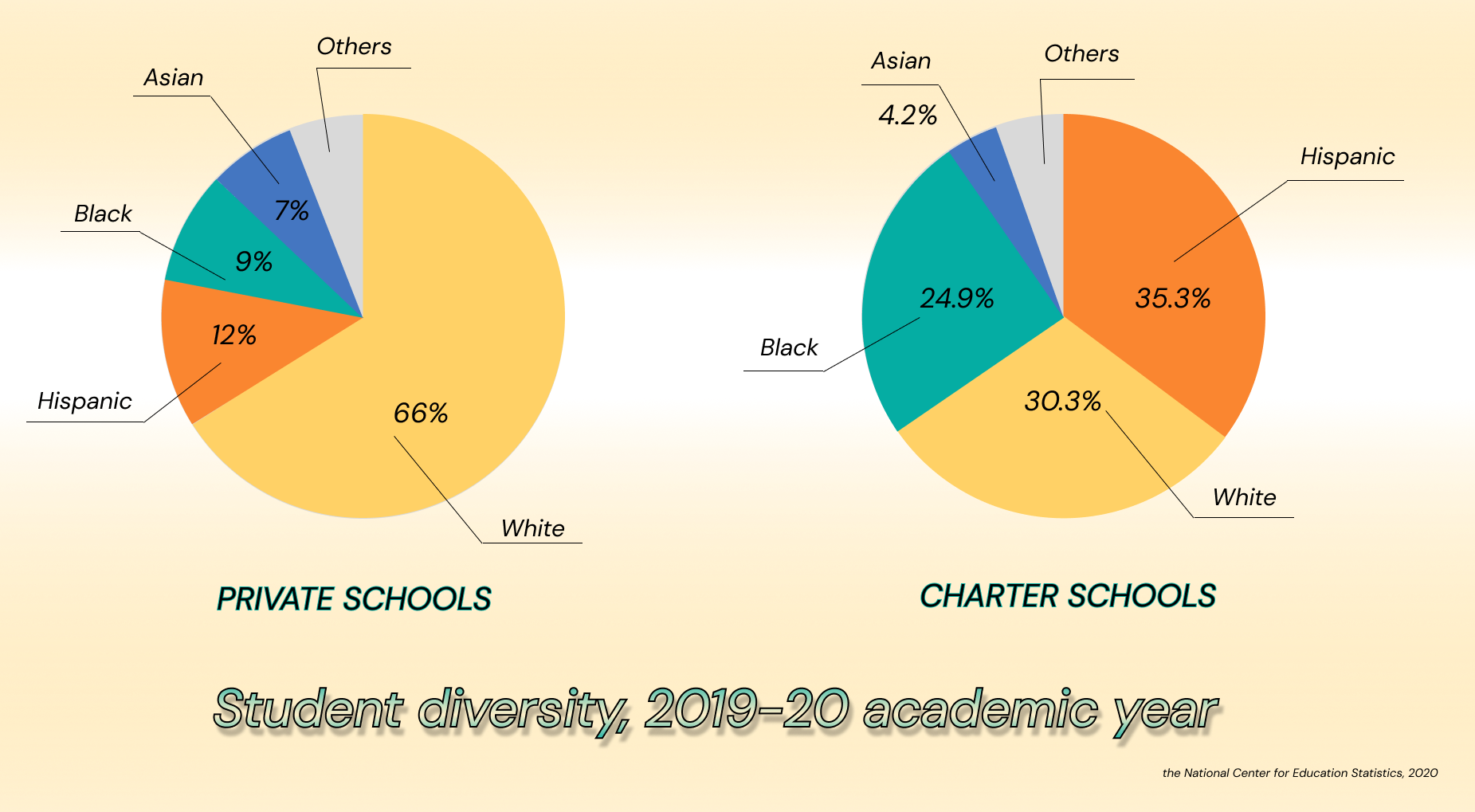
Another interesting nuance worthy of attention when identifying the difference between charter and private school is who attends these institutions. According to the National Center for Education Statistics (NCES), for the 2019-20 school year, about 60.2% of charter school students were of different racial backgrounds. Of these, 24.9% were Black, and 35.3% were Hispanic. In addition, these charter schools steadily enrolled more learners eligible for free and reduced-price lunches from 2005-06 to 2021-22.
On the other hand, private schools show a very different picture in terms of student demographics and racial diversity. In the same 2019-2020 school year, approximately 66% of private school students were white. Hispanics accounted for 12% of students, 9% were Black, 7% were Asian, and the remaining learners were of biracial, Pacific Islander, or Native American descent. The type of school funding and, of course, tuition fees played a significant role in such an arrangement of indicators.
Difference Between Private School and Charter School: Curriculum and Educational Focus
Due to diverse school funding sources and admission process peculiarities, the curriculum and scholastic focus of private and charter schools are quite different. To give you the opportunity to judge the educational quality of each institution, we have summarized the main features below.
What’s the difference between a charter school and a private school in curriculum and academic standards
Private schools:
Private schools generally have more autonomy in developing their curriculum than public charter schools. They may follow a particular educational philosophy or approach, such as Montessori, Waldorf, or religious education, due to their school funding. For significant tuition fees, their curriculum typically offers specialized programs in the arts, languages, STEM, or other areas to enrolled learners.
Charter schools:
Charter schools are publicly funded but operate independently, welcoming different student demographics. This gives them flexibility in structuring their curriculum. They must meet the academic standards outlined in their charters. Still, charter schools may experiment with innovative teaching methods, specialized programs, or alternative educational models without compromising the educational quality of the institution.
Difference between charter and private school: Religious influence and politics in schooling
Private schools:
Since private schools are completely free to include what they want in their curriculum, they may incorporate religious teachings and political agendas as long as they do not interfere with the overall educational quality. However, this is not an established fact, and most of them focus exclusively on the academic performance of their students within generally accepted subjects.
Charter schools:
As public institutions receiving state or federal school funding, charter schools must stay secular. They have no right to promote any religion or politics in their curriculum. The law obliges them to separate church and state and ensure neutrality in religious matters. Public charter schools must also be free from political influence.
Difference Between Charter and Private School: Teacher Qualifications and Teaching Standards
What’s the difference between charter school and private school in terms of teacher credentials? Teacher qualifications and teaching standards vary between charter and private schools in the following ways. Private schools typically have the autonomy to set their own hiring criteria due to their school funding type. While some of them favor having a degree and teaching certificates, others may place more emphasis on subject matter expertise or religious affiliation. Meanwhile, publicly funded charter schools must hire teachers with state-certified teacher credentials. These institutions follow standard state guidelines for teacher qualifications and licensure—and it’s important to consider how the teacher shortage affects various school systems, since funding models influence recruitment, retention, and educational quality.
Difference Between Charter and Private School: Top 3 FAQs
1. How do school funding sources impact the operations of charter and private schools? School funding sources have a significant impact on charter and private school operations. Charter schools rely on public funding, often allocated on a per-pupil basis. This affects their resources and flexibility. In contrast, private schools operate based on tuition fees, donations, and philanthropic contributions. It gives them greater financial autonomy but potentially limits their accessibility for various student demographics due to higher costs.
2. What are the differences in tuition costs and accessibility between charter and private schools? There is a major difference between charter and private school in terms of tuition fees and accessibility. Charter schools are commonly free because they receive public funding. Conversely, private schools require tuition fees, making them less affordable for low-income families.
3. How do admission criteria affect student diversity in charter and private schools? Admission criteria play a key role in shaping student diversity in private schools. Charter schools must admit all students without exception. In comparison, private schools are highly selective during the admission process. While this selectivity can influence the range of student backgrounds, it also raises broader concerns about inclusivity and equity—topics often explored in an essay sample on school safety, which may examine how diversity, school policies, and safe environments intersect to support or hinder student well-being.





